

|
PVL: Parameter Value Language
|
A Vectal is a vector of virtual objects of any type. More...
#include <Vectal.hh>
Classes | |
| class | Const_Iterator |
| A Const_Iterator provides a random access iterator for a const Vectal. More... | |
| class | Const_Reverse_Iterator |
| A Const_Reverse_Iterator provides a reverse random access iterator for a const Vectal. More... | |
| class | Iterator |
| An Iterator provides a random access iterator for a Vectal. More... | |
| class | Reverse_Iterator |
| A Reverse_Iterator provides a reverse random access iterator for a Vectal. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef Base::allocator_type | allocator_type |
| Storage allocate type (pointer allocator). | |
| typedef std::vector< T * > | Base |
| Base vector class. | |
| typedef Base::const_iterator | Base_const_iterator |
| Base vector const interator. | |
| typedef Base::const_reverse_iterator | Base_const_reverse_iterator |
| Base vector const reverse iterator. | |
| typedef Base::iterator | Base_iterator |
| Base vector iterator. | |
| typedef Base::reverse_iterator | Base_reverse_iterator |
| Base vector reverse iterator. | |
| typedef Const_Iterator | const_iterator |
| Vectal const iterator. | |
| typedef const pointer | const_pointer |
| Element const pointer. | |
| typedef const value_type & | const_reference |
| Element const reference. | |
| typedef Const_Reverse_Iterator | const_reverse_iterator |
| Vectal const reverse iterator. | |
| typedef const value_type | const_value_type |
| Element const type. | |
| typedef Base::difference_type | difference_type |
| Element pointer difference type. | |
| typedef Iterator | iterator |
| Vectal iterator. | |
| typedef value_type * | pointer |
| Element pointer type. | |
| typedef value_type & | reference |
| Element reference. | |
| typedef Reverse_Iterator | reverse_iterator |
| Vectal reverse iterator. | |
| typedef Base::size_type | size_type |
| Unsigned integral type for size values. | |
| typedef T | value_type |
| Element virtual class type. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| void | assign (size_type number, const_reference value) |
| Assigns a number of value copies. | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | assign (Iterator start, Iterator stop) |
| Assigns values from an iterator range. | |
| reference | at (size_type index) |
| Gets the indexed element. | |
| const_reference | at (size_type index) const |
| Gets the indexed element. | |
| reference | back () |
| Gets the last element. | |
| const_reference | back () const |
| Gets the last element. | |
| Iterator | begin () |
| Gets an Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the first value. | |
| Const_Iterator | begin () const |
| Gets a Const_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the first value. | |
| void | clear () |
| Removes, and destroys, all values. | |
| Iterator | end () |
| Gets an Iterator for this Vectal positioned after the last value. | |
| Const_Iterator | end () const |
| Gets a Const_Iterator for this Vectal positioned after the last value. | |
| void | erase (size_type index) |
| Removes a value at an element index position. | |
| iterator | erase (iterator start, iterator stop) |
| iterator | erase (iterator position) |
| Removes a value at an iterator position. | |
| reference | front () |
| Gets the first element. | |
| const_reference | front () const |
| Gets the first element. | |
| iterator | insert (iterator position, const_reference value) |
| Inserts a value at an iterator position. | |
| void | insert (size_type index, const_reference value) |
| Inserts a value at an element index position. | |
| void | insert (iterator position, size_type number, const_reference value) |
| Inserts a number of value copies starting at an iterator position. | |
| template<typename InputIterator > | |
| void | insert (iterator position, InputIterator start, InputIterator stop) |
| Vectal & | operator= (const Vectal< value_type > &vectal) |
| Assigns values from another Vectal. | |
| const_reference | operator[] (size_type index) const |
| Gets the indexed element. | |
| reference | operator[] (size_type index) |
| Gets the indexed element. | |
| pointer | peek (const iterator &position) |
| Gets a mutaable value pointer at an iterator position. | |
| pointer | peek (const const_iterator &position) const |
| Gets a const value pointer at an iterator position. | |
| pointer | peek_back () |
| Gets the last value pointer. | |
| pointer | peek_back () const |
| Gets the last value pointer. | |
| iterator | poke (iterator position, pointer value_pointer) |
| Inserts a value pointer (not a value copy) at an iterator position. | |
| void | poke (size_type index, pointer value_pointer) |
| Inserts a value pointer (not a value copy) at an element index position. | |
| iterator | poke (iterator position, const_iterator start, const_iterator stop) |
| void | poke_back (pointer value_pointer) |
| Pushes a value pointer (not a value copy) on the end of the Vectal. | |
| void | pop_back () |
| Removes the last value. | |
| iterator | pull (iterator position) |
| iterator | pull (iterator start, iterator stop) |
| pointer | pull_back () |
| Removes and returns the last value pointer. | |
| pointer | pull_out (size_type index) |
| pointer | pull_out (iterator position) |
| Removes the value pointer at an iterator position. | |
| void | push_back (const_reference value) |
| Pushes a value on the end of the Vectal. | |
| Reverse_Iterator | rbegin () |
| Gets a Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the last value. | |
| Const_Reverse_Iterator | rbegin () const |
| Gets a Const_Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the last value. | |
| Const_Reverse_Iterator | rend () const |
| Gets a Const_Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned before the first value. | |
| Reverse_Iterator | rend () |
| Gets a Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned before the first value. | |
| pointer | replace (iterator position, pointer value_pointer) |
| Replaces an existing element. | |
| void | resize (size_type new_size) |
| Resizes by removing excess elements, or adding new ones. | |
| void | resize (size_type new_size, const_reference value) |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| Vectal (Iterator start, Iterator stop) | |
| Construct from an Iterator range of values. | |
| Vectal (const Vectal &vectal) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| Vectal () | |
| Constructs an empty Vectal. | |
| Vectal (size_type size, const_reference value) | |
| Construct with with a number of value copies. | |
| Base & | vector_base () |
| Provides access to the base vector. | |
| void | wipe () |
| Removes all of the value pointers, but does not destroy the values. | |
| virtual | ~Vectal () |
| Destroys the Vectal and its contents. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | entering (pointer value_pointer) |
| Catches values as they are being entered into the Vectal. | |
| virtual void | removing (pointer value_pointer) |
| Catches values as they are being removed from the Vectal. | |
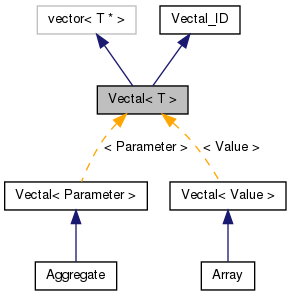
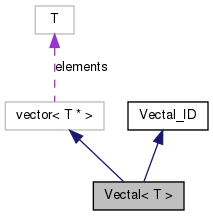
A Vectal is a vector of virtual objects of any type.
From the user's point of view a Vectal is a vector of objects of the class specified by the template parameter. The interface is essentially the same. The Vectal provides efficient storage of, and access to, objects by only storing their pointers into the corresponding vector from which it is derived. This also allows the Vectal to contain objects of pure virtual polymorphic classes which can only be used with pointers or references (since they can not be constructed directly).
More importantly, when an object is inserted into a Vectal it makes a copy of the object for internal storage. It does not copy the pointer. Since an abstract class can not be copied directly it must provide a "virtual constructor" (see Stroustrup, "The C++
Programming Language", [special edition] sect. 15.6.2) as a method named clone which takes no arguments and returns a pointer to a copy of the object. Note: The presence of the clone method is the only special requirement of a class contained in a Vectal. This method is typically implemented as follows:
class Abstract_Class {
public:
Abstract_Class (const Abstract_Class&); // Copy constructor.
virtual Abstract_Class* clone () const = 0;
...
};
class Implementing_Class : public Abstract_Class {
public:
Implementing_Class (const Implementing_Class&); // Copy constructor.
Implementing_Class* clone () {return new Implementing_Class (*this);}
...
};
Methods are provided to manipulate the object value pointers directly in the backing vector:
Note: These methods copy and delete pointers - not the objects they point to - into and out of the backing vector. The two erase methods delete the value object(s) in the Vectal before they erase the value pointer(s) directly from the Vectal; they do not use the pull methods because the intent is to destroy the erased objects, not just to remove their pointers from the Vectal.
Classes that want to control what happens to an object when it is entered or removed should subclass Vectal to override these virtual methods:
void entering (pointer value); void removing (pointer value);
Iterators are provided that implement reference semantics: their dereference (*), pointer (->) and indexing ([]) operators automatically dereference the object pointers in the backing vector. Thus, from the user's perspective the iterators appear to reference object values directly just as vector iterators do. However, instead of copying out objects as do vectors, direct object value references to the contents of the Vectal are provided.
The Vectal class is flawed. One could easily make the argument that there is no need for a Vectal; a vector of pointers to virtual types should be sufficient. However, the author wanted to provide the convenience of reference semantics, transparent reusability with different subclasses, and insert and removal hooks to the virtual class being managed to allow them to take special action for their own purposes. Thus the justification for the Vectal.
However, the Vectal does not correctly satisfy all the requirements of an STL container (see Josuttis, "The C++ Standard Library", sect. 5.10.1). In particular the elements of a Vectal are not copyable by a copy constructor. As pointed out above, the virtual elements of a Vectal require the use of a clone method for the elements of the class being managed. However the STL containers, which work with copies of their elements, use copy constructors, not a clone method. This results, at best, in object slicing at copy time. Pointers can, of course, be easily copied. But the STL containers do not, in the process, copy (i.e. clone) the object being pointed to. This can cause unacceptable problems when the user expects each element in a container to be unique.
The problem of the copy constructor for virtual classes poses a major challenge. The effect of this is that Vectals do not always work well with STL algorithms. Sorting is an excellent example: It is obviously necessary to be able to compare the values of the elements being sorted; thus using a vector of pointers to the objects to be sorted will not do. This is solved by having the Vectal iterators implement reference semantics. However, reordering elements requires that temporary copies of elements must be made. It would be fine to copy and reorder the backing pointers, but the Vectal iterators reference semantics brings up the copy constructor problem. Many STL algorithms will still work just fine with a Vectal as long as they do not have to make copies of the Vectal elements.
| typedef std::vector<T*> Base |
Base vector class.
| typedef Base::iterator Base_iterator |
Base vector iterator.
| typedef Base::const_iterator Base_const_iterator |
Base vector const interator.
| typedef Base::reverse_iterator Base_reverse_iterator |
Base vector reverse iterator.
| typedef Base::const_reverse_iterator Base_const_reverse_iterator |
Base vector const reverse iterator.
| typedef T value_type |
Element virtual class type.
| typedef const value_type const_value_type |
Element const type.
| typedef value_type& reference |
Element reference.
| typedef const value_type& const_reference |
Element const reference.
| typedef value_type* pointer |
Element pointer type.
| typedef const pointer const_pointer |
Element const pointer.
| typedef Base::size_type size_type |
Unsigned integral type for size values.
| typedef Base::difference_type difference_type |
Element pointer difference type.
| typedef Base::allocator_type allocator_type |
Storage allocate type (pointer allocator).
| typedef Const_Iterator const_iterator |
| typedef Reverse_Iterator reverse_iterator |
Vectal reverse iterator.
Vectal const reverse iterator.
| Vectal | ( | size_type | size, |
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Construct with with a number of value copies.
| size | The number of value copies with which to initialize the contents. |
| value | The value to be copied. |
Construct from an Iterator range of values.
The values in the range [start, stop) are used to intialize the contents.
| start | An Iterator positioned where the range starts (inclusive). The position is not range checked. |
| stop | An Iterator positioned where the range stops (exclusive). The position is not range checked. |
| virtual ~Vectal | ( | ) | [inline, virtual] |
Gets the indexed element.
| index | The range checked index of an element. |
| out_of_range | If the index is not in the range of existing index elements. N.B.: This exception will always be thrown if the Vectal is empty. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::at().
| const_reference at | ( | size_type | index | ) | const [inline] |
Gets the indexed element.
| index | The range checked index of an element. |
| out_of_range | If the index is not in the range of existing index elements. N.B.: This exception will always be thrown if the Vectal is empty. |
Gets the indexed element.
Unchecked - faster, but not safe - access to an indexed element.
| index | An element index of a value in the Vectal. N.B.: The validity of the index is not checked. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), Vectal< Value >::back(), Vectal< Value >::front(), and Vectal< Value >::operator[]().
| const_reference operator[] | ( | size_type | index | ) | const [inline] |
Gets the indexed element.
Unchecked - faster, but not safe - access to an indexed element.
| index | An element index of a value in the Vectal. N.B.: The validity of the index is not checked. |
| reference front | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets the first element.
N.B.: The Vectal must not be empty.
| const_reference front | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets the first element.
N.B.: The Vectal must not be empty.
| reference back | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets the last element.
N.B.: The Vectal must not be empty.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::peek_back(), Vectal< Value >::pull_back(), and Vectal< Value >::resize().
| const_reference back | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets the last element.
N.B.: The Vectal must not be empty.
Gets a mutaable value pointer at an iterator position.
| position | The iterator position to peek at. The position is not range checked. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::erase(), Vectal< Value >::pull_out(), and Vectal< Value >::replace().
| pointer peek | ( | const const_iterator & | position | ) | const [inline] |
Gets a const value pointer at an iterator position.
| position | The iterator position to peek at. The position is not range checked. |
| pointer peek_back | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets the last value pointer.
| pointer peek_back | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets the last value pointer.
| Base& vector_base | ( | ) | [inline] |
Provides access to the base vector.
| virtual void entering | ( | pointer | value_pointer | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
Catches values as they are being entered into the Vectal.
This stub does nothing by default. It should be overridden by subclasses that want to apply special handling to the object before they are entered into the Vectal.
| value_pointer | The value pointer that is being entered into the Vectal. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::poke(), Vectal< Value >::poke_back(), and Vectal< Value >::replace().
| void assign | ( | size_type | number, |
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Assigns a number of value copies.
Any existing values, up to the number being assigned, are assigned from the value provided. The value's own assignment operator is used. Any excess values are removed. A shortfall is filled with copies of the value.
| number | The number of value copies to assign. |
| value | The value to be assigned. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::operator=(), and Vectal< Value >::Vectal().
Assigns values from an iterator range.
Dereferencing (operator*) the Iterator must provide a reference to an object of the type contained by this Vectal. Existing values are replaced by assignment. Excess input values are appended. Excess existing elements are erased.
| Vectal& operator= | ( | const Vectal< value_type > & | vectal | ) | [inline] |
Assigns values from another Vectal.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::Vectal().
| iterator insert | ( | iterator | position, |
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Inserts a value at an iterator position.
A clone pointer of the value is poked into the backing vector.
| position | The iterator position where the value is to be inserted. |
| value | The value to be inserted. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::insert(), and Vectal< Value >::poke().
| void insert | ( | size_type | index, |
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Inserts a value at an element index position.
A clone pointer of the value is poked into the backing vector.
If the index is greater than or equal to the size of the Vectal the value is appended.
| index | The element index where the value is to be inserted. |
| value | The value to be inserted. |
| void insert | ( | iterator | position, |
| size_type | number, | ||
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Inserts a number of value copies starting at an iterator position.
| position | The iterator position at which to start inserting the values. |
| number | The number of value copies to insert. |
| value | The value to be inserted. |
| void insert | ( | iterator | position, |
| InputIterator | start, | ||
| InputIterator | stop | ||
| ) | [inline] |
| void push_back | ( | const_reference | value | ) | [inline] |
Pushes a value on the end of the Vectal.
A clone pointer of the value is poked into the end of the backing vector.
| value | A value reference. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), Vectal< Value >::poke_back(), and Vectal< Value >::resize().
Inserts a value pointer (not a value copy) at an iterator position.
N.B.: The value pointer is provided to the entering method before being inserted into the backing vector.
If the VECTAL_CAPACITY_MARGIN is not 0 and the allocated storage capacity has been reached, then storage reserve is increased to the next largest multiple of the margin amount.
| position | The iterator position where the value pointer will be placed. The position is not range checked. |
| value_pointer | The value pointer to be stored. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::insert(), and Vectal< Value >::poke().
Inserts a value pointer (not a value copy) at an element index position.
If the index is greater than or equal to the size of the Vectal the value is appended.
| index | The element index where the value is to be inserted. |
| value_pointer | A pointer to the value to be inserted. |
| iterator poke | ( | iterator | position, |
| const_iterator | start, | ||
| const_iterator | stop | ||
| ) | [inline] |
| void poke_back | ( | pointer | value_pointer | ) | [inline] |
Pushes a value pointer (not a value copy) on the end of the Vectal.
N.B.: The value pointer is provided to the entering method before being pushed on the end of the backing vector.
If the VECTAL_CAPACITY_MARGIN is not 0 and the allocated storage capacity has been reached, then storage reserve is increased to the next largest multiple of the margin amount.
| value_pointer | The value pointer to be stored. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::poke(), and Vectal< Value >::push_back().
| virtual void removing | ( | pointer | value_pointer | ) | [inline, protected, virtual] |
Catches values as they are being removed from the Vectal.
This stub does nothing by default. It should be overridden by subclasses that want to apply special handling to the object before they are removed from the Vectal.
| value_pointer | The value pointer that is being removed from the Vectal. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::erase(), Vectal< Value >::pull(), and Vectal< Value >::replace().
Removes a value at an iterator position.
The removed element is destroyed.
| position | The iterator position of the value to be removed. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), Vectal< Value >::clear(), Vectal< Value >::erase(), Vectal< Value >::pop_back(), Vectal< Value >::pull(), and Vectal< Value >::resize().
| void erase | ( | size_type | index | ) | [inline] |
Removes a value at an element index position.
The removed element is destroyed.
| index | An element index position. N.B.: Nothing is done ff the index is greater than or equal to the size of the Vectal. |
| void clear | ( | ) | [inline] |
Removes, and destroys, all values.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::wipe(), and Vectal< Value >::~Vectal().
| void wipe | ( | ) | [inline] |
Removes all of the value pointers, but does not destroy the values.
Warning: It is the user's responsibility to make sure that the value objects are properly managed to prevent a memory leak.
This method might be used if the value pointers have been copied elsewhere, or the value objects have already been destroyed.
| void pop_back | ( | ) | [inline] |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::erase(), Vectal< Value >::pull_back(), and Vectal< Value >::pull_out().
Removes the value pointer at an iterator position.
The value itself is not destroyed.
| position | The iterator position of the value. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::pull_out().
| pointer pull_back | ( | ) | [inline] |
Removes and returns the last value pointer.
The value itself is not destroyed.
| void resize | ( | size_type | new_size | ) | [inline] |
Resizes by removing excess elements, or adding new ones.
To increase the size a value is needed to fill the space. Virtual classes have no default constructor so the last value is used to copy into the extra space. However, if the Vectal is empty there's nothing to copy so an out_of_range error will be thrown in this case.
| new_size | The new size for the Vectal. |
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), and Vectal< Value >::resize().
| void resize | ( | size_type | new_size, |
| const_reference | value | ||
| ) | [inline] |
Replaces an existing element.
Nothing is done if the Vecatal is empty.
N.B.: The previous value pointer at the iterator position is provided to the removing method. The value is not destroyed. The new value pointer is provided to the entering method before replacing the previous pointer in the backing vector.
| position | The iterator position of the value. The position is not range checked. |
| value_pointer | The value pointer to be stored. |
| Iterator begin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets an Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the first value.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), Vectal< Value >::begin(), Vectal< Value >::clear(), Vectal< Value >::erase(), Vectal< Value >::operator=(), Vectal< Value >::poke(), and Vectal< Value >::pull_out().
| Iterator end | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets an Iterator for this Vectal positioned after the last value.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::assign(), Vectal< Value >::clear(), Vectal< Value >::end(), Vectal< Value >::operator=(), Vectal< Value >::pop_back(), Vectal< Value >::pull_back(), and Vectal< Value >::resize().
| Const_Iterator begin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets a Const_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the first value.
| Const_Iterator end | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets a Const_Iterator for this Vectal positioned after the last value.
| Reverse_Iterator rbegin | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets a Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the last value.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::rbegin().
| Reverse_Iterator rend | ( | ) | [inline] |
Gets a Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned before the first value.
Referenced by Vectal< Value >::rend().
| Const_Reverse_Iterator rbegin | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets a Const_Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned at the last value.
| Const_Reverse_Iterator rend | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Gets a Const_Reverse_Iterator for this Vectal positioned before the first value.
 1.7.4
1.7.4