 |
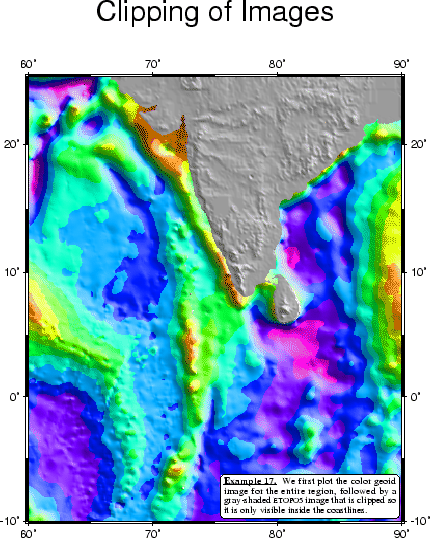
This example demonstrates how pscoast can be used to set up clippaths based on coastlines. This approach is well suited when different gridded data sets are to be merged on a plot using different color palette files. Merging the files themselves may not be doable since they may represent different data sets, as we show in this example. Here, we lay down a color map of the geoid field near India with grdimage, use pscoast to set up land clippaths, and then overlay topography from the ETOPO5 data set with another call to grdimage. We finally undo the clippath with a second call to pscoast with the option -–Q (Figure 6.17):
grd2cpt india_geoid.grd -Crainbow >! geoid.cpt grdgradient india_geoid.grd -Nt1 -A45 -Gindia_geoid_i.grd grdimage india_geoid.grd -Iindia_geoid_i.grd -JM6.5i -Cgeoid.cpt -P -K -U"Example 17 in Cookbook" \ >! example_17.ps pscoast -R60/90/-10/25 -JM -O -K -Dl -Gc >> example_17.ps echo "-10000 150 10000 150" >! gray.cpt grdgradient india_topo.grd -Nt1 -A45 -Gindia_topo_i.grd grdimage india_topo.grd -Iindia_topo_i.grd -JM -Cgray.cpt -O -K >> example_17.ps pscoast -R -JM -O -K -Q -B10f5:."Clipping of Images": >> example_17.ps pstext -R -JM -O -M -W255O0.5p -D-0.1i/0.1i << EOF >> example_17.ps > 90 -10 12 0 4 RB 12p 3i j @_@%5%Example 17.@%%@_ We first plot the color geoid image for the entire region, followed by a gray-shaded @#etopo5@# image that is clipped so it is only visible inside the coastlines. EOF \rm -f geoid.cpt gray.cpt *_i.grd .gmt*