|
|
Start of Tutorial > Start of Trail > Start of Lesson | Search |
This section answers four questions:
JFC is short for JavaTM Foundation Classes, which encompass a group of features to help people build graphical user interfaces (GUIs). The JFC was first announced at the 1997 JavaOne developer conference and is defined as containing the following features:
- The Swing Components
- Include everything from buttons to split panes to tables. You can see mugshots of all the components in A Visual Index to the Swing Components
.
- Pluggable Look & Feel Support
- Gives any program that uses Swing components a choice of looks and feels. For example, the same program can use either the JavaTM Look & Feel or the Windows Look & Feel. We expect many more look-and-feel packages -- including some that use sound instead of a visual "look" -- to become available from various sources.
- Accessibility API
- Enables assistive technologies such as screen readers and Braille displays to get information from the user interface.
- Java 2DTM API (JDK 1.2 only)
- Enables developers to easily incorporate high-quality 2D graphics, text, and images in applications and in applets.
- Drag and Drop Support (JDK 1.2 only)
- Provides the ability to drag and drop between a Java application and a native application.
The first three JFC features were implemented without any native code, relying only on the API defined in JDK 1.1. As a result, they could and did become available as an extension to JDK 1.1. This extension was released as JFC 1.1, which is sometimes called "the Swing release." The API in JFC 1.1 is often called "the Swing API."
Note: "Swing" was the codename of the project that developed the new components. Although it's an unofficial name, it's frequently used to refer to the new components and related API. It's immortalized in the package names for the Swing API, which begin withjavax.swing.This trail concentrates on the Swing components. We help you choose the appropriate ones for your GUI, tell you how to use them, and give you the background information you need to use them effectively. We discuss the Pluggable Look & Feel and Accessibility support when they affect how you write Swing programs. This trail does not cover the JFC features that appear only in JDK 1.2. For information about those, refer to 2D Graphics
and to the JFC Home Page.
The following snapshots show three views of a GUI that uses Swing components. Each picture shows the same program, but with a different look and feel. The program, called
Converter, is discussed in detail at the end of the next lesson, Swing Features and Concepts.
Java Look & Feel CDE/Motif Look & Feel 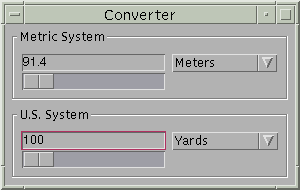
Windows Look & Feel
The Swing API is present in two releases:
- JDK 1.2
- JFC 1.1 (for use with JDK 1.1)
Which release you use depends on whether you need to use JDK 1.1 or JDK 1.2. It's a bit simpler to use JDK 1.2: because the JFC is built into JDK 1.2 and you don't need to add libraries to be able to use the Swing API. However, if you need to use JDK 1.1, then adding the Swing API (using JFC 1.1) isn't difficult. Instructions for doing both are in Compiling and Running Swing Programs.
This trail describes the Swing 1.1 API, which is the version present in JDK 1.2 FCS and in the release called "JFC 1.1 (with Swing 1.1)." The code in this trail works, without any changes, with either release.
Sun has released many versions of JFC 1.1, which are identified by the version of Swing API they contain. One previous version, for example, was called "JFC 1.1 (with Swing 1.0.3)." The following table shows some of the important releases containing Swing API. Bold font indicates the releases typically used in shipping products.
Swing API version Corresponding
JFC 1.1 releaseCorresponding
JDK 1.2 releaseComments Swing 0.2 JFC 1.1
(with Swing 0.2)none The first public release of JFC 1.1. Swing 1.0.3 JFC 1.1
(with Swing 1.0.3)none The release of JFC 1.1 included in Java Plug-inTM 1.1.1. Supported for use in shipping products. Swing 1.1 Beta JFC 1.1
(with Swing 1.1 Beta)JDK 1.2 Beta 4 The first JDK 1.2 release that used the same Swing package names as the corresponding JFC 1.1 release. Swing 1.1 Beta 3 JFC 1.1
(with Swing 1.1 Beta 3)JDK 1.2 RC1 The first release with the final Swing package names. Swing 1.1 Note: This is the API this trail covers.
JFC 1.1
(with Swing 1.1)JDK 1.2 FCS The first releases containing the final Swing 1.1 API supported for use in shipping products. Java Plug-in 1.1.2 and Java Plug-in 1.2 provide applet support for JDK 1.1 + Swing 1.1 and JDK 1.2, respectively.
The Swing API is powerful, flexible -- and immense. For example, the JFC 1.1 release has 15 public packages:javax.accessibility,javax.swing,javax.swing.border,javax.swing.colorchooser,javax.swing.event,javax.swing.filechooser,javax.swing.plaf,javax.swing.plaf.basic,javax.swing.plaf.metal,javax.swing.plaf.multi,javax.swing.table,javax.swing.text,javax.swing.text.html,javax.swing.tree, andjavax.swing.undo.Fortunately, most programs use only a small subset of the API. This trail sorts out the API for you, giving you examples of common code and pointing you to methods and classes you're likely to need. Most of the code in this trail uses only one or two Swing packages:
javax.swingjavax.swing.event(not always required)
If you don't care about the AWT components, skip to the next section. You can get a more general introduction to the Swing components from A Quick Tour of a Swing Application's Code and from the Swing Features and Conceptslesson.
The AWT components are those provided by the JDK 1.0 and 1.1 platforms. Although JDK 1.2 still supports the AWT components, we strongly encourage you to use Swing components instead. You can identify Swing components because their names start with
J. The AWT button class, for example, is namedButton, while the Swing button class is namedJButton. Additionally, the AWT components are in thejava.awtpackage, while the Swing components are in thejavax.swingpackage.The biggest difference between the AWT components and Swing components is that the Swing components are implemented with absolutely no native code. Since Swing components aren't restricted to the least common denominator -- the features that are present on every platform -- they can have more functionality than AWT components. Because the Swing components have no native code, they can be be shipped as an add-on to JDK 1.1, in addition to being part of JDK 1.2.
Even the simplest Swing components have capabilities far beyond what the AWT components offer:
- Swing buttons and labels can display images instead of, or in addition to, text.
- You can easily add or change the borders drawn around most Swing components. For example, it's easy to put a box around the outside of a container or label.
- You can easily change the behavior or appearance of a Swing component by either invoking methods on it or creating a subclass of it.
- Swing components don't have to be rectangular. Buttons, for example, can be round.
- Assistive technologies such as screen readers can easily get information from Swing components. For example, a tool can easily get the text that's displayed on a button or label.
Swing lets you specify which look and feel your program's GUI uses. By contrast, AWT components always have the look and feel of the native platform.
Another interesting feature is that Swing components with state use models to keep the state. A
JSlider, for instance, uses aBoundedRangeModelobject to hold its current value and range of legal values. Models are set up automatically, so you don't have to deal with them unless you want to take advantage of the power they can give you.If you're used to using AWT components, you need to be aware of a few gotchas when using Swing components:
- Programs should not, as a rule, use "heavyweight" components alongside Swing components. Heavyweight components include all the ready-to-use AWT components (such as
MenuandScrollPane) and all components that inherit from the AWTCanvasandPanelclasses. This restriction exists because when Swing components (and all other "lightweight" components) overlap with heavyweight components, the heavyweight component is always painted on top. For more information, see Mixing Heavy and Light Components, an article in The Swing Connection.- Swing components aren't thread safe. If you modify a visible Swing component -- invoking its
setTextmethod, for example -- from anywhere but an event handler, then you need to take special steps to make the modification execute on the event-dispatching thread. This isn't an issue for many Swing programs, since component-modifying code is typically in event handlers.- The containment hierarchy for any window or applet that contains Swing components must have a Swing top-level container at the root of the hierarchy. For example, a main window should be implemented as a
JFrameinstance rather than as aFrameinstance.- You don't add components directly to a top-level container such as a
JFrame. Instead, you add components to a container (called the content pane) that is itself contained by theJFrame.Converting to Swing
tells you more about the differences between Swing components and AWT components.
|
|
Start of Tutorial > Start of Trail > Start of Lesson | Search |